Log Mean Temperature Difference Analysis
Section 11.3
Log Mean Temperature Difference Analysis is a heat exchanger analysis method that can be used if you know the inlet and outlet temperatures of your hot and cold fluids and one of the mass flow rates. You can then calculate the heat transfer between the fluids and the overall heat transfer coefficient.
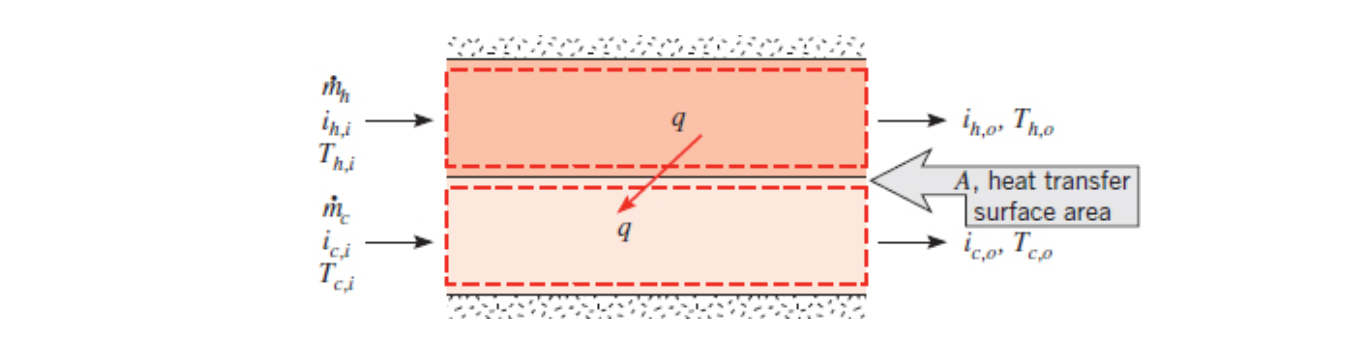
Energy balance of the hot fluid (Equation 11.6a):
Energy balance of the cold fluid (Equation 11.7a):
Where
If the fluids stay in the same phase and you can assume a constant specific heat as they change temperature then you can use temperature instead of enthalpy:
Energy balance of the hot fluid (Equation 11.6b):
Energy balance of the cold fluid (Equation 11.7b):
Where
See ME3304 S24 Lecture Note (6) Heat Exchanger and 12A - 2nd Class for more information.
See ME3304 S24 Lecture Note (6) Heat Exchanger, page 21 for information about how to determine the mean temperature.
If you need to find the heat-exchanger-overall-heat-transfer-coefficient you can use equation 11.14:
Where
Log Mean Temperature Difference is defined in equation 11.15:
For a counter flow heat exchanger they are defined by equation 11.17:
Special Operating Conditions
Section 11.3.3